Key Takeaways
- Cybercrime is a growing threat, costing a projected $10.5 trillion globally by early 2025.
- AI tools have enabled faster and sneakier data breach strategies.
- AI tools can also help prevent those attacks and protect manufacturers from cybersecurity threats.
AI, automation, the Internet of Things, robotics, and more offer significant benefits for manufacturers and distributors. But as digital maturity accelerates, so does risk. These same technologies create new entry points for attackers and expand the potential impact of a breach.
With the deployment of new technologies ranking number one in our most recent mid-market manufacturing outlook report, it’s more critical than ever to focus on cybersecurity and risk awareness.
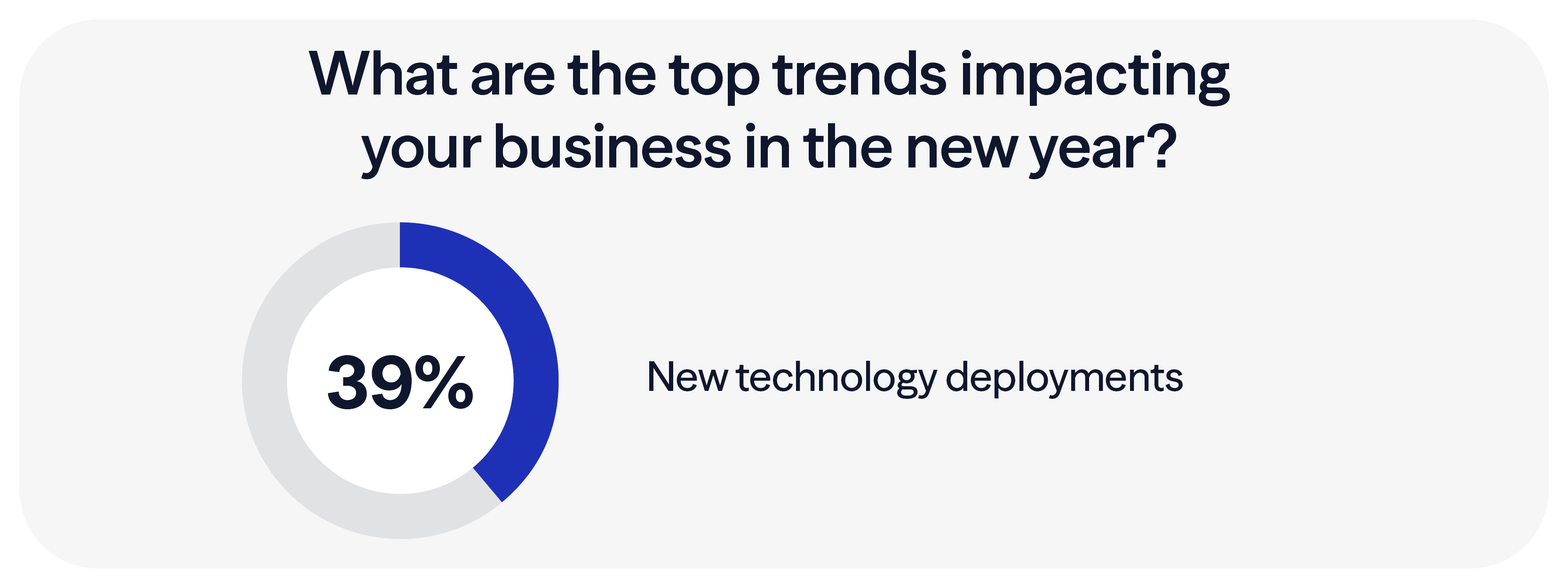
Fortunately, manufacturing leaders are taking the new threats seriously. In our 2026 Mid-Market Manufacturing Outlook, 31% of respondents reported an increased focus on cybersecurity and data privacy, up from 24% in 2025. Additionally, 75% of respondents plan to increase investments in cybersecurity solutions in the next year.
The Rise of Cyber Risk
Cybercrime continues to escalate, costing the global economy approximately $10.5 trillion annually. Gartner also projects that spending on information security will increase to $240 billion this year, underscoring the urgency of protecting your digital environment.
The rise of AI is a significant contributor, with 94% of companies citing it as the number one driver of change in cybersecurity in the years ahead, according to the World Economic Forum.
For manufacturers, the risk extends beyond traditional IT systems. Legacy equipment, disconnected technologies, and complex supply chains create a patchwork of vulnerabilities. Yet only 29% of surveyed leaders are increasing risk management and scenario planning, and just 28% are prioritizing workforce upskilling — gaps that widen exposure.
Here's how to prioritize risk awareness and stay competitive in manufacturing.
Ways to Reduce Your Cyber Risk
Implement Zero Trust Architecture
As threats evolve, trust-based security is no longer sufficient. A Zero Trust approach — “never trust, always verify” — requires continuous verification for any user, machine, or service attempting access. This framework strengthens defenses across both IT and OT environments.
Strengthen Operational Technology (OT) Security
A Fortinet study found that half of operational technology-based organizations were victims of cyber breaches. Manufacturers and distributors are particularly vulnerable, as they function with numerous interconnected, and potentially exposed, networks and environments.
To mature your OT posture:
- Elevate OT security as a strategic leadership priority
- Develop a targeted cybersecurity roadmap for OT environments
- Increase visibility across systems and phase out legacy devices
- Assess risk through uptime, safety, compliance, and regulatory impacts
Utilize AI
Criminals use AI to perform faster, more sophisticated data breaches, but you also can use it to thwart their efforts. It starts with performing a security threat assessment on the current system.
Manufacturers should monitor:
- Completion of cybersecurity training by employees
- Threat detection counts and response times
- Login anomalies, such as spikes in failed attempts
AI-enabled tools help close security gaps by continuously analyzing activity and autoresponding to emerging threats. SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) is an ideal framework that aggregates data across the organization and deploys automated remediation actions in real time.
Prep for Automation Readiness
To automate effectively, review your technology setup and target integration gaps.
Key steps:
- Assess your tech stack and identify manual security workflows
- Define success criteria for secure automation
- Stress test automation protocols against existing safeguards
- Upskill teams to understand new tools and potential risks
Once you’ve taken the steps to implement AI effectively, use automation to:
- Detect abnormal machine behavior
- Shut down compromised endpoints
- Monitor compliance with industry standards like NIST and CMMC
Vendor Risk Management
Your security standards must apply beyond your actual company. Because supply chains are deeply interconnected, a single vendor with weak controls can expose your entire operation. Audit each vendor and ensure they align with strict security standards.
Protect Your Manufacturing Organization
Cybercrime tends to keep up with current technology trends, giving bad actors more efficient ways to access sensitive information. The good news is that the same technology that enables criminals also offers businesses the tools to stop them.
The most proactive manufacturers will be those who unify their approach to cybersecurity governance (and have leadership buy-in), enforce necessary principles for security and identity of humans and machines, and focus on operational continuity, not just IT impacts.
Learn how emerging trends in mid-market manufacturing can help your organization plan for what’s next. Get the report.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is cybersecurity becoming a bigger issue for manufacturers in 2026?
Manufacturers are constantly dealing with legacy equipment and disconnected technologies on the shop floor, opening them to further risk. Also, manufacturers are adopting more AI, automation, IoT, and connected systems, which increases the attack surface. At the same time, attackers are using AI to automate and accelerate cyberattacks.
What types of cyber threats most commonly affect manufacturing organizations?
Top threats include ransomware, business email compromise, OT system intrusions, supply chain breaches, credential theft, and AI-generated phishing attacks.
How does AI increase cyber risk?
AI enables criminals to create more targeted attacks, break into systems faster, automate credential stuffing, and mimic human behavior to avoid detection.
How can AI help defend against cyberattacks?
AI security tools can detect anomalies, identify attempted intrusions, automate responses, and monitor OT environments in real time.
What is Zero Trust, and why is it important for manufacturers?
Zero Trust requires verification before granting access to any system or device — crucial in environments with interconnected machinery and remote access entry points.
How can manufacturers reduce cybersecurity vulnerabilities in legacy equipment?
Manufacturers should improve visibility, segment networks, implement OT-specific security tools, and upgrade or isolate outdated devices.
Why is vendor risk management important?
A breach in any supplier can impact your entire production ecosystem. Auditing vendor cybersecurity is essential for protecting the supply chain.
How can manufacturers get started improving cybersecurity?
Start with a security risk assessment, evaluate OT maturity, train employees, implement Zero Trust, and address high-priority vulnerabilities.
2026 Mid-Market Manufacturing Outlook Report

Manufacturing, Distribution, and Logistics
Rely on the trusted expertise of manufacturing advisors to help you build and execute your strategic vision.
Cybersecurity
Eide Bailly’s cybersecurity team provides guidance, strategic direction, and prioritization of business objectives and cyber risks.
Who We Are
Eide Bailly is a CPA firm bringing practical expertise in tax, audit, and advisory to help you perform, protect, and prosper with confidence.


